
Instead, we may state our results “provide support for” or “give evidence for” our research hypothesis (as there is still a slight probability that the results occurred by chance and the null hypothesis was correct – e.g. Analyze, graph and present your scientific work easily with GraphPad Prism. You should note that you cannot accept the null hypothesis, we can only reject the null or fail to reject it.Ī statistically significant result cannot prove that a research hypothesis is correct (as this implies 100% certainty). Use this calculator to compute a P value from a Z, t, F, r, or chi-square value that you obtain from a program or publication. Due to the means of the two jumps and the direction of the t-value, we can conclude that there was a statistically significant improvement in jump distance following the plyometric-training programme from 2.48 ± 0.16 m to 2.52 ± 0.16 m (p < 0.0005) an improvement of 0.03 ± 0.03 m. This means we retain the null hypothesis and reject the alternative hypothesis. In our case this would be: t(19) -4.773, p < 0.0005. If the p-value is below your threshold of significance (typically p 0.05) is not statistically significant and indicates strong evidence for the null hypothesis. Therefore, we reject the null hypothesis, and accept the alternative hypothesis. It indicates strong evidence against the null hypothesis, as there is less than a 5% probability the null is correct (and the results are random).
#How to calculate p value in spss 16 how to
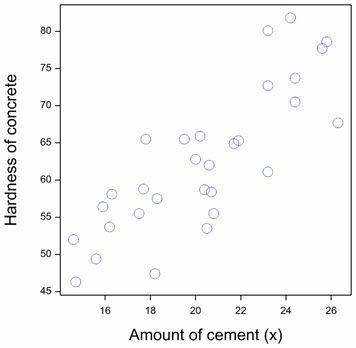
A p-value less than 0.05 (typically ≤ 0.05) is statistically significant. ANOVA (Analysis of Variance) explained in simple terms. Running head: Application: Chi-Square with SPSS (Statistical Software) 1 How to Calculate Chi-Square with SPSS (Statistical Software) V.V.L.N.The smaller the p-value, the stronger the evidence that you should reject the null hypothesis. The level of statistical significance is often expressed as a p-value between 0 and 1. How do you know if a p-value is statistically significant?Ī p-value, or probability value, is a number describing how likely it is that your data would have occurred by random chance (i.e.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
